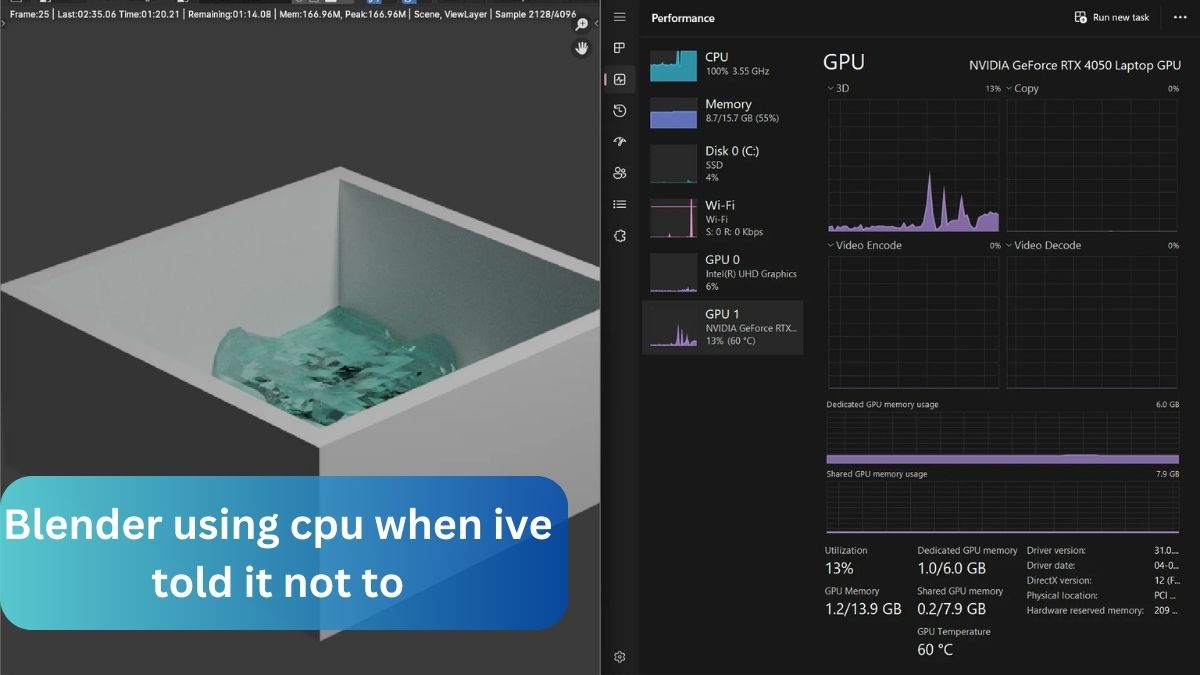
Blender might use the CPU instead of the GPU if the settings aren’t properly configured. Go to Edit > Preferences > System and ensure the GPU is selected under Cycles Render Devices. Also, update your GPU drivers and check if your GPU is compatible with Blender. These steps should resolve the issue.
When I faced the issue of Blender using CPU when I’ve told it not to, it turned out I hadn’t selected my GPU in the preferences. After updating my drivers and enabling GPU rendering, everything worked smoothly.
In this article, we will discuss “Blender using cpu when ive told it not to”.
Table of Contents
Understanding Blender’s CPU and GPU Usage
Blender uses both the CPU and GPU for different tasks. While the CPU handles things like simulations and general processing, the GPU is optimized for rendering. Ideally, for high-quality and speedy renders, the GPU is your go-to option.
Why Blender Might Be Using the CPU Instead of GPU
There are several reasons Blender might default to the CPU:
- Incorrect settings: Your Blender preferences might not be configured properly.
- Compatibility issues: Your GPU may not meet Blender’s requirements.
- Outdated drivers: Using old drivers can prevent Blender from accessing your GPU efficiently.
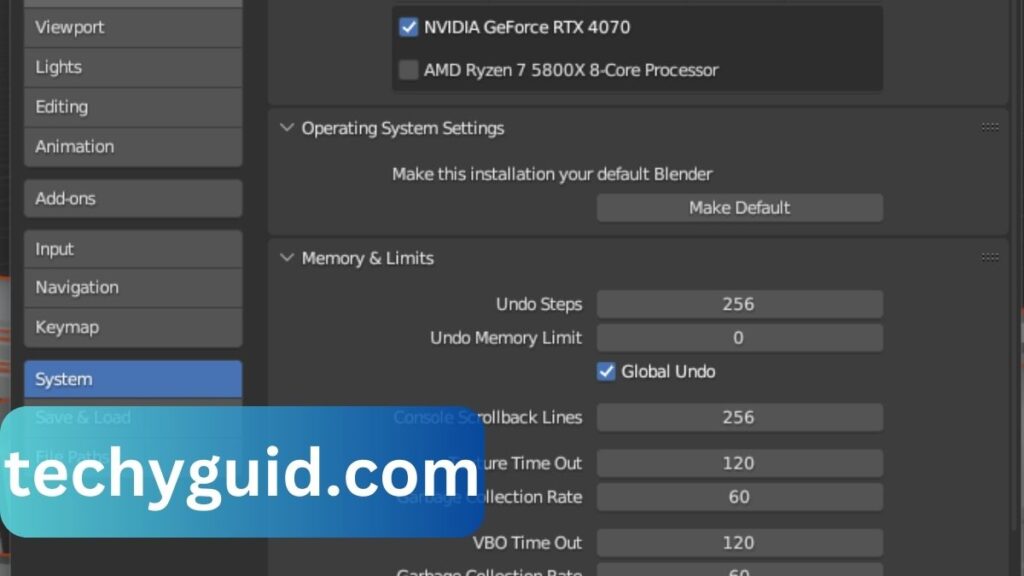
Checking Your Blender Preferences
Here’s how to ensure Blender is set up to use your GPU:
- Open Blender and go to Edit > Preferences.
- Click on System.
- Under Cycles Render Devices, ensure your GPU (CUDA, OptiX, or HIP) is selected.
Read Most Important: Do AVX CPU Cores Fixed on Mac – Ultimate Guide 2024!
Updating Your Graphics Drivers
Outdated drivers are a common culprit. Follow these steps:
- Identify your GPU model (e.g., NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel).
- Visit the official website of your GPU manufacturer.
- Download and install the latest drivers.
- Restart Blender and verify the settings.
Ensuring GPU Compatibility with Blender
Blender supports specific GPUs, depending on their architecture and memory. Verify that your GPU is on Blender’s list of supported devices, and ensure it has sufficient VRAM for rendering.
System Resource Allocation
Sometimes, your operating system may allocate tasks inefficiently, forcing Blender to rely on the CPU. You can adjust system settings to prioritize your GPU for intensive tasks.
Common Mistakes When Configuring Blender
Users often overlook critical settings, like enabling GPU rendering in cycles or choosing the correct compute device. Double-check your configurations to avoid these pitfalls.
How to Enable GPU Rendering in Blender
To enable GPU rendering:
- Open Blender and switch to the Cycles rendering engine.
- Go to Preferences > System.
- Under Render Devices, select your GPU.
- Start a render and monitor the resource usage.
Performance Differences: CPU vs. GPU Rendering
GPU rendering is generally faster and more efficient for complex scenes. However, the CPU may still handle certain calculations better, depending on your project’s requirements.
Troubleshooting Blender’s Resource Usage
If Blender continues to use your CPU:
- Check your system logs for errors.
- Reset Blender’s preferences.
- Test on a different version of Blender to rule out bugs.
Advanced Settings for Optimizing Blender Performance
For demanding projects:
- Allocate more VRAM by closing background applications.
- Use denoising tools to speed up rendering.
- Enable experimental features if you’re comfortable with potential instability.
Third-Party Tools and Plugins to Enhance Performance
Tools like MSI Afterburner can monitor your GPU usage, while plugins like E-Cycles offer optimized rendering options for Blender.
Real-Life Examples and Solutions
A user once faced this exact issue when working on a high-poly scene. After updating their drivers and enabling CUDA, their render times improved by 50%.
Read Most Important: wall mounted industrial cabinet with cpu modules – Full Guide 2024!
Blender using CPU instead of GPU
Blender might use the CPU instead of the GPU if the preferences are not set to use the GPU. Go to Edit > Preferences > System, and under Cycles Render Devices, select your GPU. Update your drivers and ensure your GPU is compatible with Blender.
Blender using 100% CPU
If Blender is using 100% CPU, it’s likely handling tasks like physics simulations or rendering without GPU support. Check your preferences and enable GPU rendering to offload some work to the GPU.
Blender not using GPU
Blender may not use your GPU if it’s not selected in the settings or if the GPU is incompatible. Ensure GPU rendering is enabled in Edit > Preferences > System and that your drivers are up to date.
Blender not using full CPU
Blender might not use the full CPU if the task doesn’t require it or if your system limits CPU usage for multitasking. You can optimize settings and ensure no background processes are restricting performance.
Blender not using full GPU
Blender might not use the full GPU if the project isn’t GPU-intensive or if there’s a bottleneck in VRAM. Check that the GPU is properly configured in the preferences and close unnecessary applications.
Blender CPU
The CPU in Blender handles various tasks like simulations, modifiers, and viewport performance. While rendering is faster on a GPU, CPUs are still vital for many operations.
How to set Blender to use GPU
To set Blender to use the GPU, go to Edit > Preferences > System, select your GPU under Cycles Render Devices, and enable GPU rendering in the render properties.
Blender 4.0 not using GPU
If Blender 4.0 isn’t using your GPU, check for bugs in the version, verify GPU compatibility, and ensure your drivers are updated. Also, double-check the preferences to enable GPU rendering.
How to get Blender to use GPU instead of CPU?
Go to Edit > Preferences > System in Blender, select your GPU under Cycles Render Devices, and enable GPU rendering in the render properties. Update your GPU drivers to ensure compatibility.
Why is Blender using CPU?
Blender defaults to the CPU if the GPU isn’t selected in preferences or if the GPU is incompatible. Check your settings and verify your GPU is supported and up-to-date.
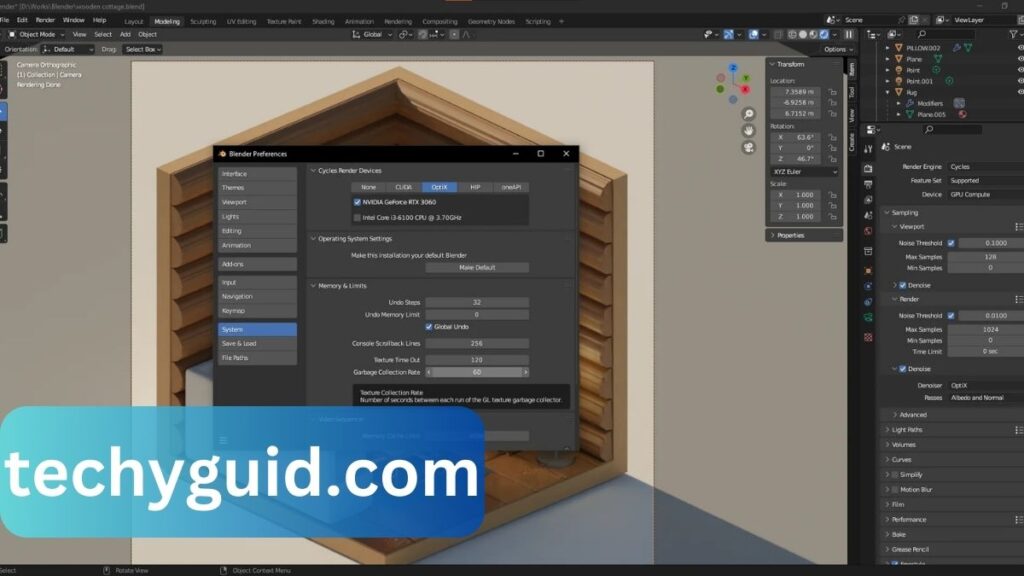
Can an RTX 3060 run Blender?
Yes, the RTX 3060 is fully compatible with Blender and performs well for GPU rendering due to its CUDA and OptiX support.
Is it better to use CPU or GPU for Blender render?
GPU rendering is faster and more efficient for complex scenes, while CPU rendering handles certain simulations and operations better. For speed, go with GPU.
How do I only use GPU instead of CPU?
In Blender, switch to Cycles Render Engine, then go to Edit > Preferences > System and select your GPU. This ensures the GPU handles rendering tasks.
Which is better, CUDA or OptiX?
OptiX is faster and more optimized for modern NVIDIA GPUs with ray-tracing cores, while CUDA is widely compatible. Use OptiX if your GPU supports it.
Why Blender is not using GPU?
Blender may not use the GPU if it’s not selected in the settings, your GPU isn’t compatible, or the drivers are outdated. Check preferences and ensure proper configuration.
Read Most Important: pascal safety calculator result pdf – Ultimate Guide 2024!
Does Blender use RAM or CPU?
Blender uses both. The CPU handles calculations, and RAM is crucial for storing scene data during complex projects.
Why use food processor instead of Blender?
A food processor is better for chopping, slicing, and dough-making, while a blender is ideal for liquids and smoothies. Each has specific uses.
Is 3D rendering CPU or GPU intensive?
3D rendering can be both CPU and GPU intensive, depending on the rendering engine. Cycles in Blender is GPU-optimized, while the CPU is used for tasks like simulations and physics calculations.
Which GPU is best for Blender?
High-end GPUs like NVIDIA RTX 4090 or 3090 are excellent for Blender due to their CUDA and OptiX support, large VRAM, and exceptional rendering speeds.
How do I make Blender use less GPU?
To reduce GPU usage in Blender, lower render samples, simplify scenes, reduce textures, and use denoising features. These changes ease the GPU’s workload.
How much CPU do I need for Blender?
A multi-core CPU like the AMD Ryzen 9 5900X or Intel i9-12900K is ideal for Blender, as it benefits from higher core counts for simulations and multi-threaded tasks.
Is Blender CPU or GPU intensive Reddit?
Blender is primarily GPU-intensive for rendering, especially with Cycles. However, the CPU handles physics, simulations, and certain modifiers. Both are important.
Is Blender a heavy software?
Yes, Blender can be heavy, especially for large scenes or detailed renders. It demands a powerful CPU, GPU, and sufficient RAM for smooth performance.
Does Blender rely on CPU or GPU?
Blender relies on both. The GPU is crucial for rendering, while the CPU handles simulations, viewport performance, and background tasks.
Is 12GB of VRAM enough for 3D rendering?
Yes, 12GB of VRAM is sufficient for most 3D rendering tasks, including complex scenes, unless dealing with extremely high-resolution textures or massive simulations.
Is RTX 3060 better than 4060 for 3D rendering?
The RTX 4060 generally offers better performance due to newer architecture and features, but the RTX 3060 has more VRAM (12GB vs. 8GB), which can be crucial for large projects.
Why won’t Blender use GPU?
Blender won’t use the GPU if it’s not selected in preferences, the GPU is incompatible, or drivers are outdated. Ensure GPU rendering is enabled in Edit > Preferences > System.
Which cycle render device to choose?
Choose CUDA or OptiX for NVIDIA GPUs, HIP for AMD GPUs, and Metal for macOS devices. OptiX is the fastest for compatible NVIDIA GPUs.
How to render faster in Blender?
Use GPU rendering, reduce sample counts, enable denoising, use simpler shaders, and optimize scene complexity to speed up rendering.
How to use GPU instead of CPU for Blender?
In Blender, go to Edit > Preferences > System, select your GPU under Cycles Render Devices, and switch the render engine to Cycles in the properties panel.
Is it better to use CPU or GPU for rendering?
GPU rendering is faster and more efficient for most tasks, but CPUs are better for certain simulations and tasks that require precision.
What CPU is good for Blender?
High-core-count CPUs like the AMD Ryzen 9 5950X or Intel Core i9-13900K are excellent for Blender, offering great performance for simulations and multi-threaded tasks.
Is GTX or RTX better for Blender?
RTX GPUs are better due to their support for OptiX and ray tracing, providing faster and more efficient rendering compared to GTX cards.
Can Blender use both CPU and GPU?
Yes, Blender can use both CPU and GPU simultaneously with hybrid rendering, which can be enabled in the Cycles render settings.
Is an RTX 4060 good for 3D rendering?
Yes, the RTX 4060 is good for 3D rendering, offering solid performance with OptiX support, but its 8GB VRAM may limit performance for very large scenes.
Does Blender use a lot of CPU?
Yes, Blender uses a lot of CPU for tasks like simulations, modifiers, and some rendering tasks if GPU rendering isn’t enabled.
How much VRAM is needed for Blender?
8GB of VRAM is sufficient for most Blender projects, but 12GB or more is ideal for handling complex scenes or high-resolution textures.
How many cores for Blender CPU?
Blender benefits from multi-core CPUs. A CPU with 8 to 16 cores is ideal, but higher core counts improve performance for heavy simulations and rendering.
Read Most Important: Can You Use 70 Isopropyl Alcohol To Clean The CPU – Ultimate Guide 2024!
FAQs
1. Why does Blender default to CPU rendering?
Blender might default to CPU rendering if the GPU isn’t selected in preferences or if your GPU isn’t supported.
2. Can Blender use both CPU and GPU simultaneously?
Yes, Blender can utilize both in certain scenarios, but this requires enabling hybrid rendering.
3. How do I check if my GPU is active in Blender?
Monitor GPU activity through Blender’s System Console or a tool like Task Manager.
4. What are the best GPUs for Blender rendering?
High-end GPUs like the NVIDIA RTX series or AMD Radeon Pro are excellent choices.
5. How do I optimize Blender for low-end hardware?
Use simpler shaders, reduce sample counts, and enable denoising to improve performance.
Conclusion
Blender defaulting to CPU usage can be frustrating, but with the right settings and troubleshooting, you can ensure smooth, GPU-powered rendering. Take it step by step, and you’ll be back to creating amazing projects in no time.
Read Most Important: